As we’ve reached the milestone of the three-year anniversary of the ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity (CC) credential, let’s take a few moments to get to know the professionals who hold this credential. With more than 67,000 certified CC holders worldwide, this group is diverse in age, location and professional backgrounds, and a significant portion already have strong foundations of IT and cybersecurity experience.
Experienced Professionals Hold the CC
The CC credential was launched in 2022 with the intention of helping those who earn it demonstrate an aptitude to learn cybersecurity skills to employers. With no pre-requisite work experience, the credential plays a unique role in the ISC2 portfolio, being accessible to those not already working in the field.
However, ISC2 and employers are learning that many CC holders already in the field view the certification as an opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge, skills and abilities as they look to advance their careers within IT and cybersecurity.
According to ISC2 data, some 45% of CC holders reported already working in cybersecurity. Of those who worked in cybersecurity prior to getting certified, the median work experience was six years. For those working in IT – not cyber – before getting certified, the median work experience was 10 years. Additionally, for those coming from outside of both cyber and IT, the median work experience was 10 years.
“After many years as an IT Manager, handling IT security tasks in daily operations and implementing ISMS - I finally took the time to certify this experience with the Certified in Cybersecurity (CC) certification from ISC2. Huge thanks to ISC2 for the excellent learning resources, and to all my amazing colleagues who support me every day - your collaboration makes all the difference!” - Antje Zoschke, CC
What Roles Do CCs Have
Based on current job listings at the time of writing, as well as industry insights, here are common roles employers are hiring for that cite the ISC2 CC as a preferred qualification:
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
- Information Security Analyst
- Cyber Threat Analyst
- Technical Support Engineer (with a security focus)
- IT Security Analyst
- Incident Responder
- Junior Penetration Tester
- Risk and Compliance Analyst
- Security Administrator
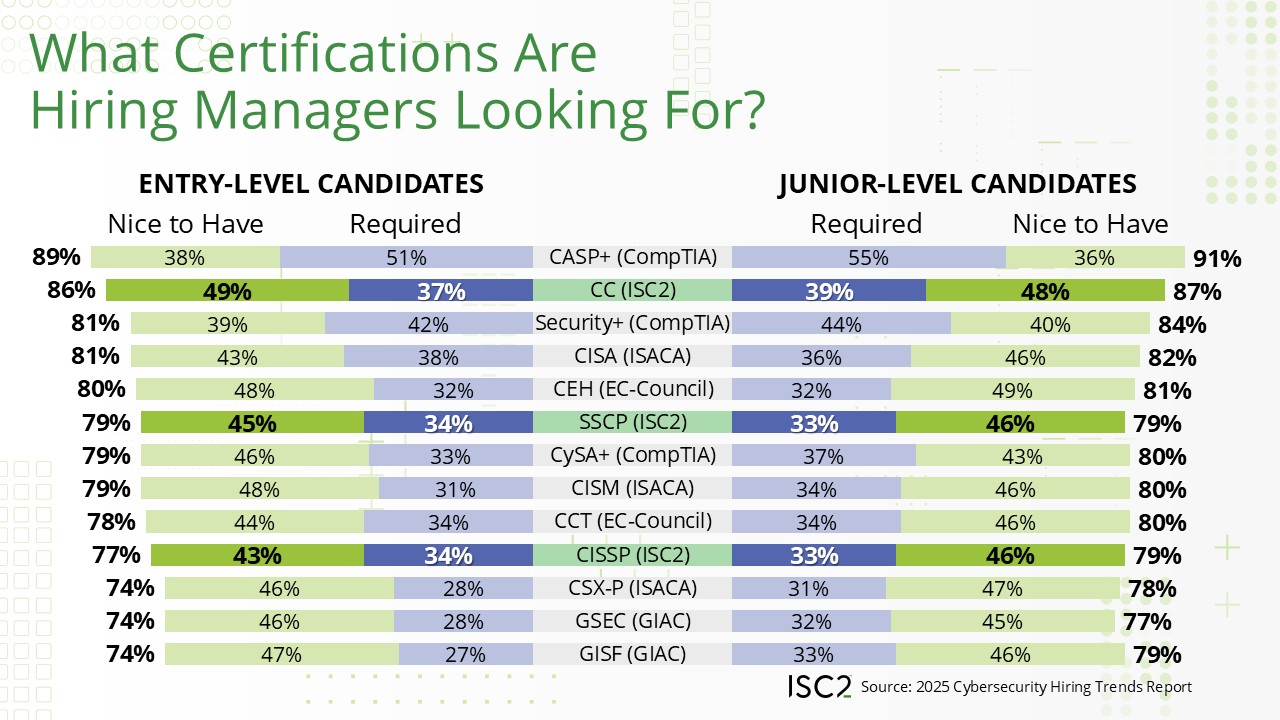
Security managers who are hiring entry- and junior-level employees look for the CC credential when evaluating candidates. When combining "required” and “nice to have,” the certification already ranks second on the list, a resounding endorsement of the quality of the certification, and those who hold it, especially considering how new it is to the industry.
Another sign of endorsement of the credential from employers is the financial benefit to certification holders. Some 10% of CC holders working in cybersecurity roles surveyed said they received a salary increase, while 7% said they received a promotion, both within their first certification cycle.
CC holders we surveyed also are committed to continuing their professional growth, as well, with 54% planning to pursue an additional certification in the next 6-12 months. This aligns strongly with data from the latest Cybersecurity Workforce Study, which showed that 90% of respondents who earned their first cybersecurity certification before their first job in cybersecurity found it either valuable or very valuable for their careers.
Certified in Cybersecurity Textbook
Preparing for the Certified in Cybersecurity exam? Consider the Official ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity (CC) eTextbook to add to your study journey. This textbook provides a comprehensive review of the topics covered in the Official ISC2 CC Training Course, plus chapter overviews, objectives and summaries, informative graphics, key terms and definitions, chapter quizzes and more.


